difference between autoclave and filtered|sterilization by filtration : Chinese Aerosol Barrier tips, also called filter pipette tips, are fitted with a filter inside the proximal part of the tip. The filter protects your pipettes from aerosols and aspirating volatile or viscous solutions into the barrel, all of which can contaminate and damage the pipette. These tips usually come pre-sterilized and DNase/RNase-free. ↑ Hasło „autoklaw” w: Elżbieta Pieńkos, Jerzy Pieńkos, Leon Zaręba, Jerzy .
{plog:ftitle_list}
eficacy is highly dependent upon actual temperature. For example, if a steam autoclave is running at 120°C for 15 minutes, the theoretical lethality of that cycle is only 82% of a cycle running at .
Autoclaving is technically your best bet, but in a pinch sterile filtering is fine. For the base media, autoclaving sometimes is required, I’ve found with the Middlebrook because it’s such a small amount per volume it is fine to just sterile filter it.
The two basic types of steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the gravity . At a glance. Sterilizing practices from the Guideline for Disinfection and .1 FILTRATION Selecting the Best Filter for Your Application Choosing a filter does not have to be complicated – Corning has simplified the process. Just follow these four easy steps: Step 1: Match your application with the appropriate pore size. Step 2: Select the membrane and housing material for your application. Step 3: Select the correct membrane area to optimize flow rate . Aerosol Barrier tips, also called filter pipette tips, are fitted with a filter inside the proximal part of the tip. The filter protects your pipettes from aerosols and aspirating volatile or viscous solutions into the barrel, all of which can contaminate and damage the pipette. These tips usually come pre-sterilized and DNase/RNase-free.
Major Differences between Autoclave and Dry Heat Sterilizer Autoclaves are sterilizing devices which use pressure, temperature and time to eliminate any microbial presence in the instruments. On the other hand, dry .
sterilization by filtration
sterile membrane filter
Sterilization can be sometimes tricky and unpredictable. While some choose to boil their equipment, most professionals would rather use steam sterilization by either a pressure cooker or a steam sterilizer (or autoclave). Sterilization is a procedure used to kill or physically remove microorganisms and their various resistant reproductive spores. What is the difference between a horizontal and vertical autoclave? While a horizontal autoclave features a chamber that’s horizontally oriented and accessed via the front of the unit, a vertical autoclave’s chamber is vertically oriented and top-loading. Autoclave sterilizer belongs to this type of equipment. Autoclave sterilizers are designed to kill all life forms on surfaces such as fungi, spores, viruses and bacteria. Autoclaves use steam only for disinfection, while others may use high pressure, irritants, chemicals, filtration, or a combination of processes to sterilize surfaces.Counter pressure autoclaves. Terminal treatment of solutions in . sealed containers. Aim is to "neutralize" the effects of the . overpressure. Liquid load in hermetically sealed containers . Two types of processes: • superheated water autoclave (also, “water cascade”, or “water rain”) • air-over-steam. autoclave (also, “steam .
The main meaning of filter is derived from the field of chemistry: “to pass (a liquid, gas, light, or sound) through a device to remove unwanted”. It this meaning, filtrate and filter are absolutely synonymous. In specific uses, such as “people filtered out of the room” or “news began to filter in from the hospital”, it sounds rather weird to use filtrate. Depyrogenation is the process of removing or inactivating pyrogens, whereas sterilization is the process of eliminating all forms of microbial life. Understanding the differences between these processes is important for ensuring product safety, which may help to prevent the patients from Harmful Pathogens. 3. Filter pad/ Pre-filter. A filter pad is present on the top of the cabinet through which the air passes into the cabinet. The filter pad traps dust particles and some microbes from entering the working environment within the cabinet. 4. Fan/ Blower. A fan is present below the filter pad that sucks in the air and moves it around in the cabinet.
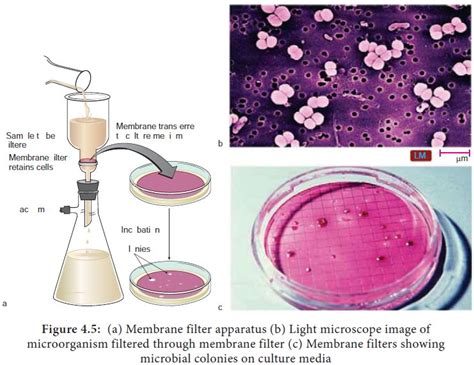
A study from the British Journal of Dentistry showed that after a single day’s use, the level of gram-negative bacteria, as well as endotoxins, reached unacceptable levels in benchtop autoclave water reservoirs. 2 Thus, not only is ensuring proper operation of an autoclave critical, but regular, daily maintenance is required to ensure patient safety.Differences between hydrophilic membranes and hydrophobic membranes. A hydrophobic membrane, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) will resist any aqueous sample, creating back pressure. Although it is sometimes possible to overcome this back pressure with additional force, there is a risk of membrane rupture and incomplete filtration.
membrane filtration sterilization
In the comparison between distilled water and filtered water, filtered water emerges as the better option for everyday hydration. It provides a balance between removing contaminants and preserving essential minerals, offering improved taste and overall water quality. By opting for filtered water, you can enjoy clean, safe, and balanced hydration. A chemical fume hood protects the user while a biosafety cabinet protects the user, the environment, and the material. Biosafety cabinets have high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters while chemical fume hoods do not. The HEPA filter in the exhaust system of a biosafety cabinet will effectively trap all known infectious agents and ensure that only microbe .
The contaminated air is then pushed below the workbench and taken upwards to the plenum. From the plenum the air is passed through the HEPA filter. Usually 30% of the air will be sent back to the environment through the HEPA filter the remaining 70% of the air passes through another hepa filter and enters the working surface of the cabinet.Know the difference between autoclaving and sterilization, benefits of steam sterilization, what is gamma or e-beam radiation, why sterilization is necessary for medical devices, and cost of autoclaves. DUNS 87-234-4128 [email protected]. We are ETO Sterilizer Specialist +91-9712379703 . For most applications, a positively charge 0.22-micron filter will be sufficient. For stricter applications, a dual layer 0.22 or even 0.10 micron charged filter might be a better option. Testing frequency. How often the process will be . HEPA is a type of pleated mechanical air filter. It is an acronym for "high efficiency particulate air [filter]" (as officially defined by the U.S. Dept. of Energy).This type of air filter can theoretically remove at least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and any airborne particles with a size of 0.3 microns (µm).
kartell pasteur pipette
The difference between pasteurization and sterilization can be identified under following major categories: . irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Autoclave is a widely used method for heat sterilization and it generally uses the following time-temperature combination 121 °C at 100 kPa for about 3 to 15 minutes, to sterilize a product An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure/temperature. Autoclaves are used in medical applications to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis.However, there are some key differences between the two. An autoclave is a specialized piece of equipment that is commonly used in laboratories and medical facilities to sterilize equipment and materials. Autoclaves use high pressure steam to sterilize materials, and they often reach temperatures of 121-134 degrees Celsius (250-273 degrees . Step 4: Filter the Solution. Hold the assembled syringe and filter it upright. Filter the solution into the receiving bottle by slowly pressing down the syringe plunger to push the sample through the filter. Note: Avoid pressing excessively as this could cause the filter housing to burst. Step 5: Filter more Samples
Generally, a filter is considered to be a sterilizing filter when, after being challenged with 1.0 x 10 7 challenge organisms per square centimetre of effective filter area (EFA), the resulting filtrate is sterile. The two basic types of steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the gravity displacement autoclave and the high-speed prevacuum sterilizer. In the former, steam is admitted at the top or the sides of the sterilizing chamber and, because the steam is lighter than air, forces air out the bottom of the chamber through the drain vent. The World Health Organization recommends autoclave cycles run between 121 and 124 C for 15 minutes at about 30 PSI. This should be enough time to kill any microorganism. Autoclaves are common place in most labs and are an obvious choice for many applications. Drawbacks include overhead costs for the autoclave, as well as utility costs to run .
Biological safety cabinets contain a filter known as high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter, which is a type of depth filter. . Difference Between (19) General Microbiology (102) Immunology (57) Lab Equipment (61) MCQs (30) . Autoclave Sterilization: Principle, Procedure, Types, . Apple cider vinegar is simply a vinegar made from apple juice or apple cider. It comes in two versions: filtered and unfiltered. The difference between the two is the “mother,” which is a somewhat murky collection of cellulose and acetic acid bacteria that’s removed when the vinegar is filtered. Does it matter which type of vinegar you use? Much depends on what .
filter used for sterile filtration
Water quality is a key factor in ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of autoclaves. Autoclaves rely on steam to sterilize surgical instruments and equipment, so using .
difference between autoclave and filtered|sterilization by filtration